Bioequivalence: The proven efficacy of phenylbutyrate and phenylacetate
OLPRUVA was shown to be bioequivalent to sodium phenylbutyrate powder in two phase 1 pharmacokinetic studies7
Two phase 1 studies were conducted in healthy adult volunteers (N=37), using a single-dose (5 g of active ingredient, ie, sodium phenylbutyrate), 3-period, 3-sequence crossover design. Study drugs were given on days 1-37:
- In Study 1, subjects received OLPRUVA with a high-fat meal (fed), OLPRUVA fasted, and sodium phenylbutyrate powder fasted; OLPRUVA was prepared with modified Mix-Aid†
- In Study 2, subjects received OLPRUVA with Mix-Aid† and sodium phenylbutyrate powder—all under fed conditions
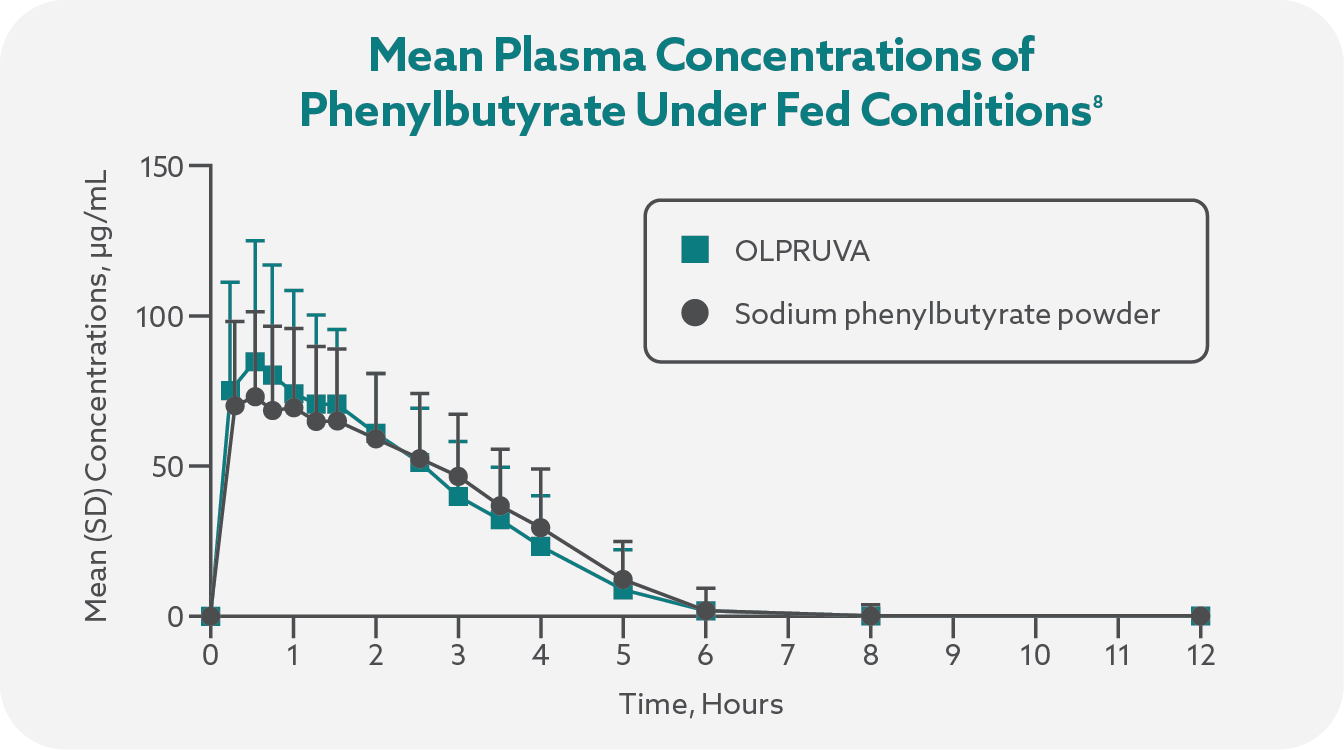
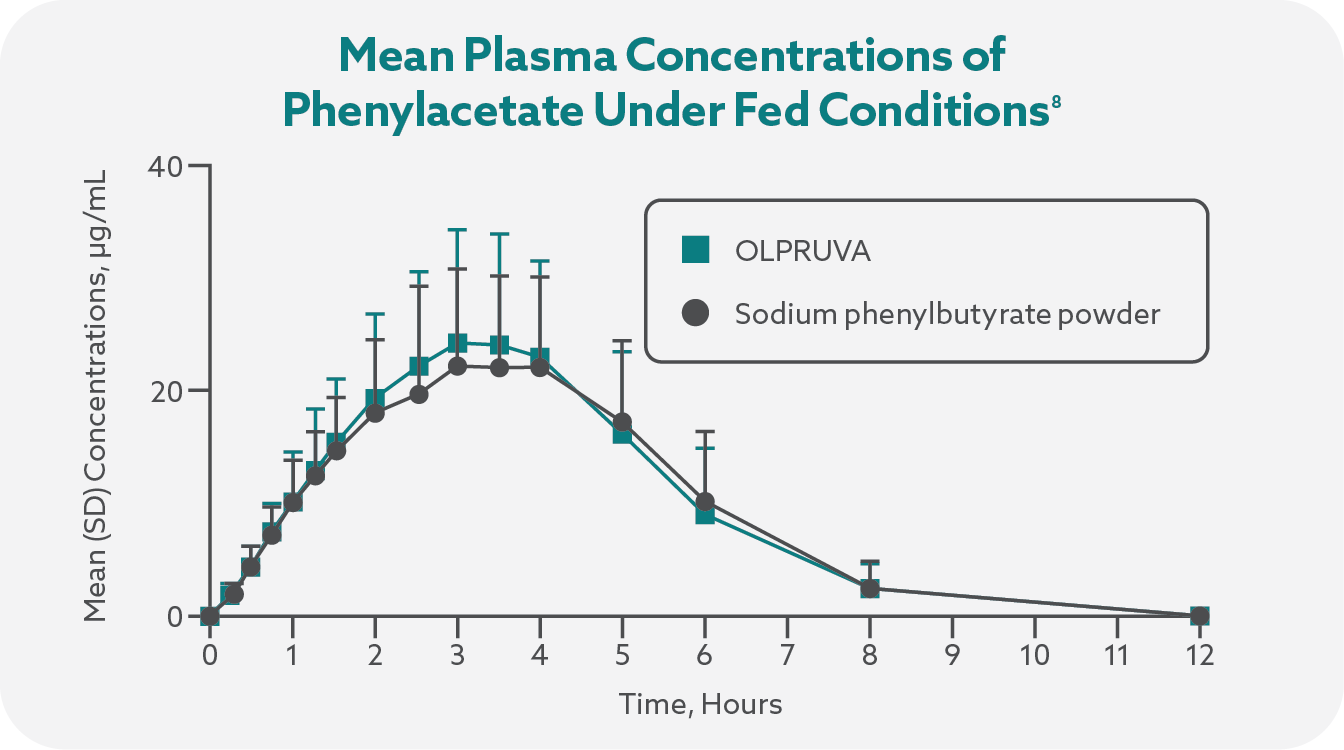
Plasma concentrations of phenylbutyrate and the active metabolite phenylacetic acid (PAA) were determined using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry, and plasma samples were collected from all subjects prior to dosing and at multiple timepoints following study-drug administration.7
†Mix-Aid (called Thick-It in the phase 1 studies) is 100% modified food starch used in commercially available OLPRUVA.
OLPRUVA is rapidly converted into the active metabolite phenylacetate, which allows for removal of ammonia.1
Increased exposure to phenylacetate, the major metabolite of OLPRUVA, may be associated with neurotoxicity in patients with UCDs. OLPRUVA is not approved for intravenous use or for treatment of patients with cancer. If neurotoxicity symptoms of vomiting, nausea, headache, somnolence, or confusion are present in the absence of high ammonia levels or other intercurrent illnesses, consider reducing the dose of OLPRUVA.
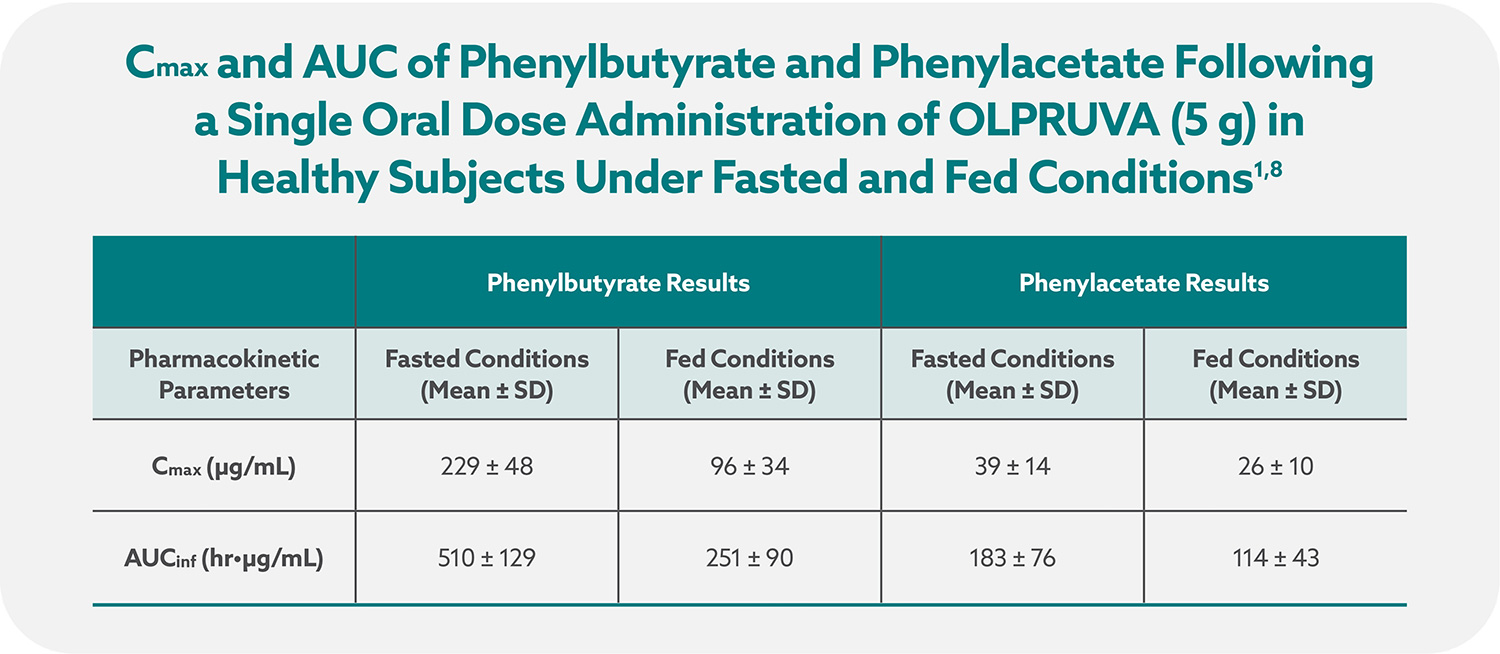
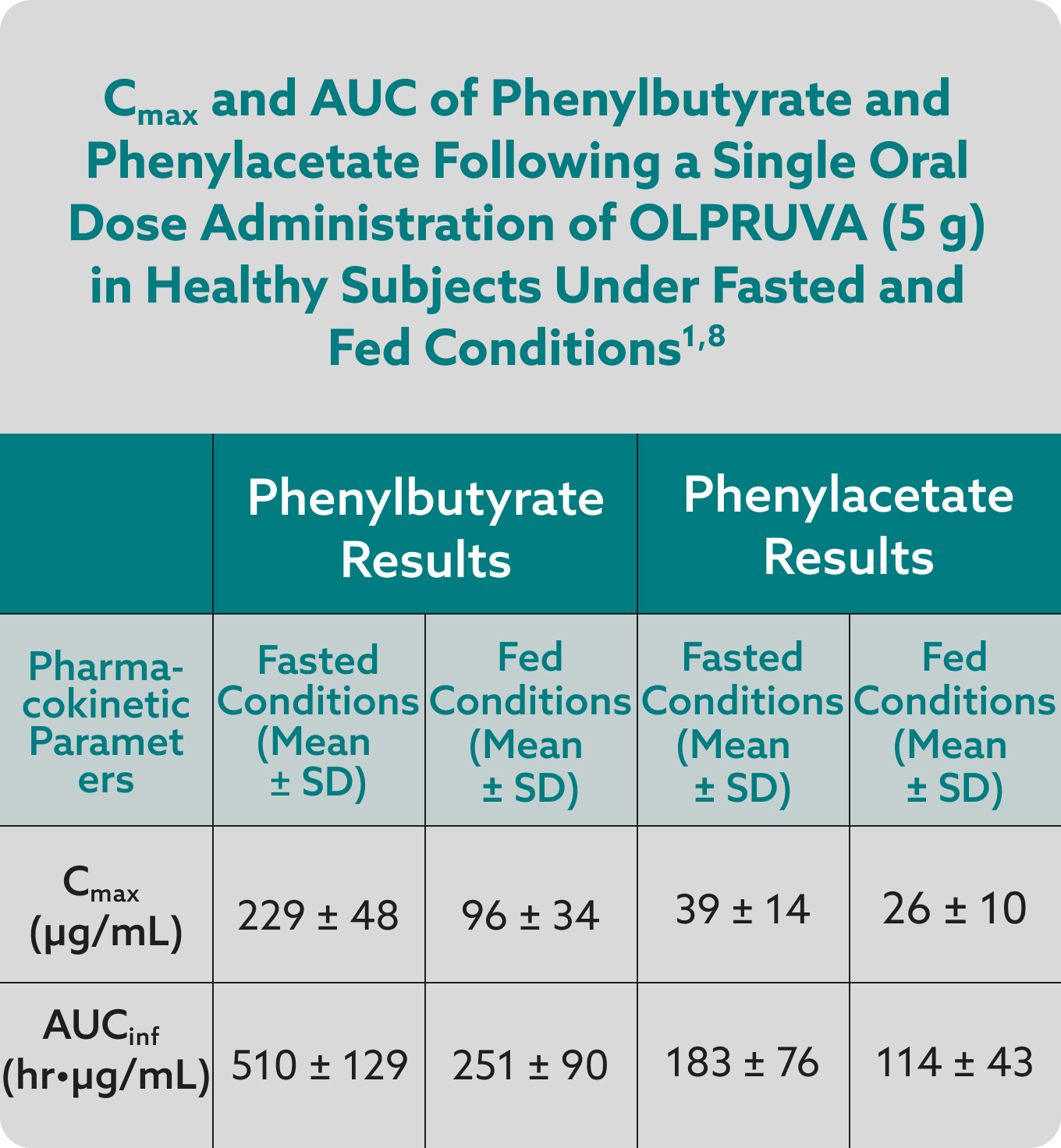
Total systemic exposures (AUCinf) and peak exposures (Cmax) of phenylbutyrate and phenylacetate were bioequivalent for OLPRUVA and sodium phenylbutyrate powder in the fasted and fed states.1,7
OLPRUVA should always be taken with food. Under fasted conditions, the Cmax and AUCinf were increased by 50% and 39%, respectively, for phenylbutyrate and 32% and 29%, respectively, for phenylacetate when compared to when OLPRUVA was administered with a high-fat meal.‡
The maximum recommended daily dose for OLPRUVA is 20 grams.1
‡These data were derived from mean values for Cmax and AUCinf.